About Us
THE NANOMEL PROJECT
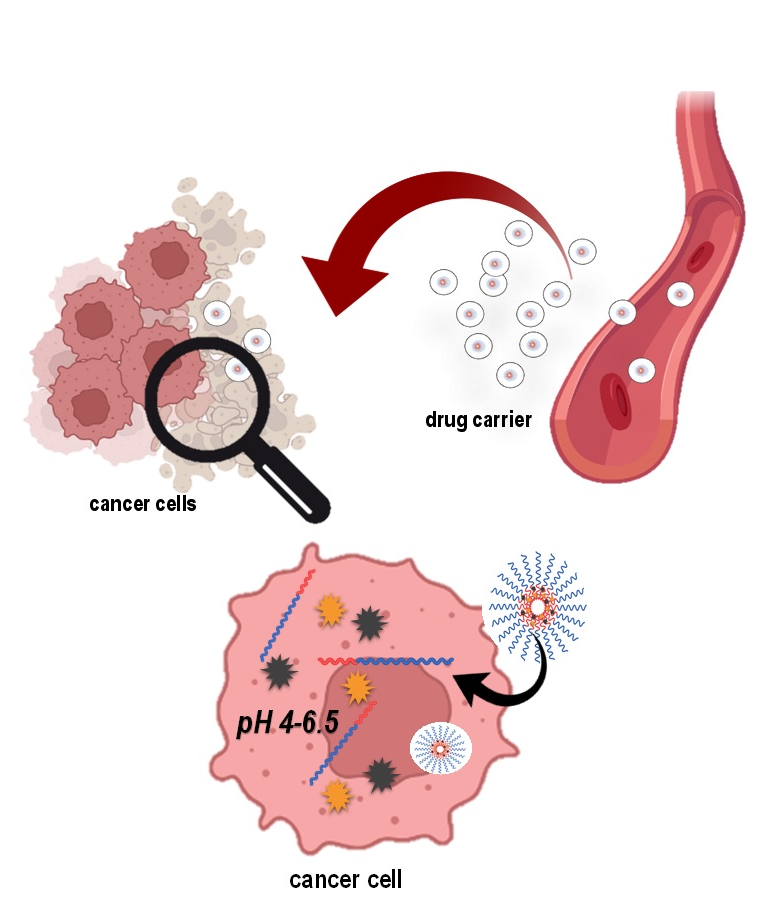
Melanoma is a type of cancer that develops in the melanin-producing cells called melanocytes. There are many possible treatments offered to patients nowadays, however, due to the metastatic nature of the cells in addition to their resistance to drugs, effective therapy of melanoma still remains poor. Further to shedding light on the mechanism of drug delivery to cells, Nanomel project combines state of the art knowledge on nanoparticle-based drug delivery aiming at improving therapy by developing polymeric nanocarrier systems in an innovative way for targeting melanoma cells, preserving minimum peripheral exposure and increasing anticancer efficacy. More specifically, novel amphiphilic diblock copolymers are synthesized bearing Doxorubicin (DOX) and Paclitaxel (PTX) to their hydrophobic side chains. DOX and PTX are two clinically well-established and highly effective anti-neoplastic drugs that are widely used as a combination therapy due to their synergistic effects. These two anti-cancer agents are attached to the polymers’ side-chains via a hydrazone bond, a dynamic covalent bond with dual nature that can be as labile as a non-covalent bond at acidic pH, or as permanent as a covalent bond under neutral pH. Consequently, due to cancer inner cell acidic environment (acidic pH) compared to healthy melanocyte neutral environment, the use of a hyrazone bond helps reduce the possibility of premature drug release. In addition to the pH dependent drug release, an anti-PMEL17 antibody is also employed, targeting PMEL17, a protein highly expressed on melanoma cell surface. PMEL17 is a promising target for melanoma cells since it seems to be absent in healthy melanocytes. Lastly, the synthesized polymeric nanocarriers are being evaluated for cell internalization, cytotoxicity and their possible effect on cell migration.
CONCEPT OF NANOMEL
Increasing efficacy through combination therapy: The innovation of our proposal is to synthesize polymer drug conjugates with two drugs attached on the same polymer chain. DOX and PTX have been reported to work well as sequential combination therapy in free form.
Using pH-responsive polymer drug conjugates: Since the intracellular environment of the cancerous
cell is more acidic than a healthy cell, drugs are attached via an acid-sensitive hydrazone bond, by exploiting the acidic pH conditions which exist within cancer cells.
Targeting melanoma through a specific monoclonal antibody: Additionally, the proposed pH responsive polymer-drug conjugate will bear a monoclonal antibody (anti-PMEL17) targeting a disease specific antigen called PMEL17, thus improving specificity.